Description
Efficient Dry Granulation with Roller Compactor
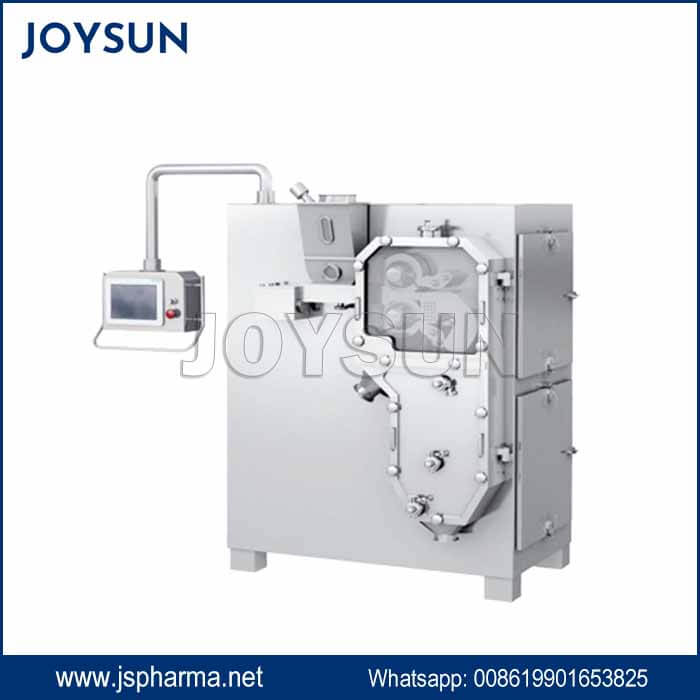
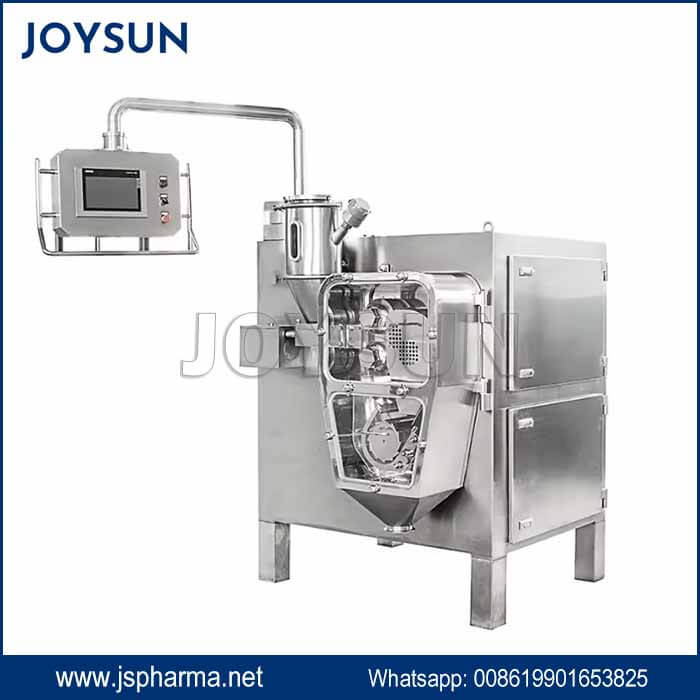
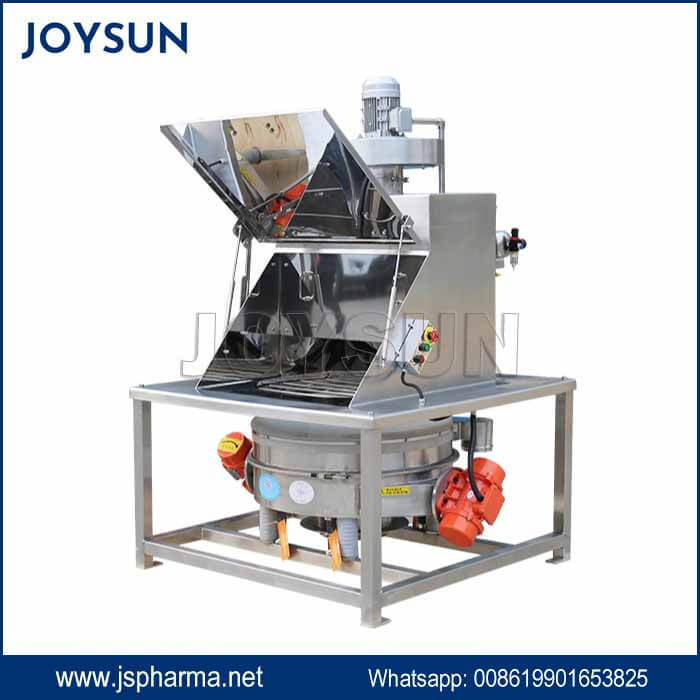
What A typical roller compactor setup involves?
How does the dry granulation roller compactor work?
The final granules size is crucial due to below factors
What factors influence the dry granulating process
What Advantages does Dry Granulation Have?
What industires is Dry Roller Compaction used?
Roller Compactor for Dry Granulation Introduction
The roller compactor is a versatile machine that simplifies the granulation process. It continuously feeds and discharges material, combining extrusion, crushing, and granulation into a single step. This technology directly presses powdered materials into uniform granules.
Dry granulation roller compactor excels at granulating materials that pose challenges in traditional methods. It’s ideal for materials that are wet, heat-sensitive, prone to decomposition, or have a tendency to clump together.
This efficient process has found widespread application in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food production, and chemicals.
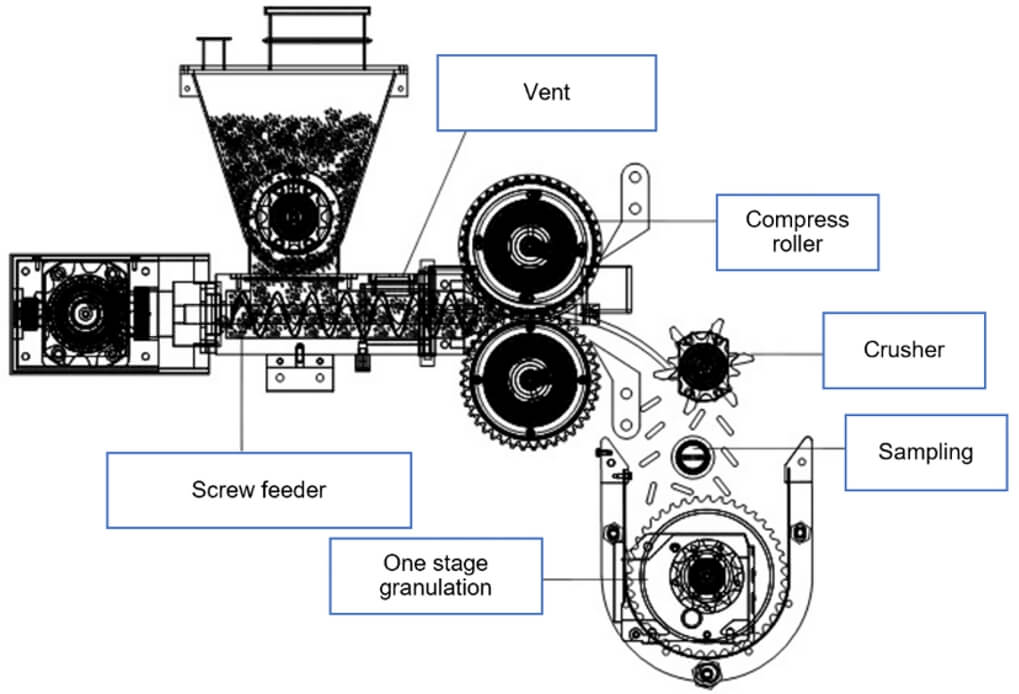
What A typical roller compactor setup involves?
- Feeding System: Delivers a consistent flow of powder to the compaction chamber.
- Compaction chamber: Two counter-rotating rollers compress the powder into a sheet or flake.
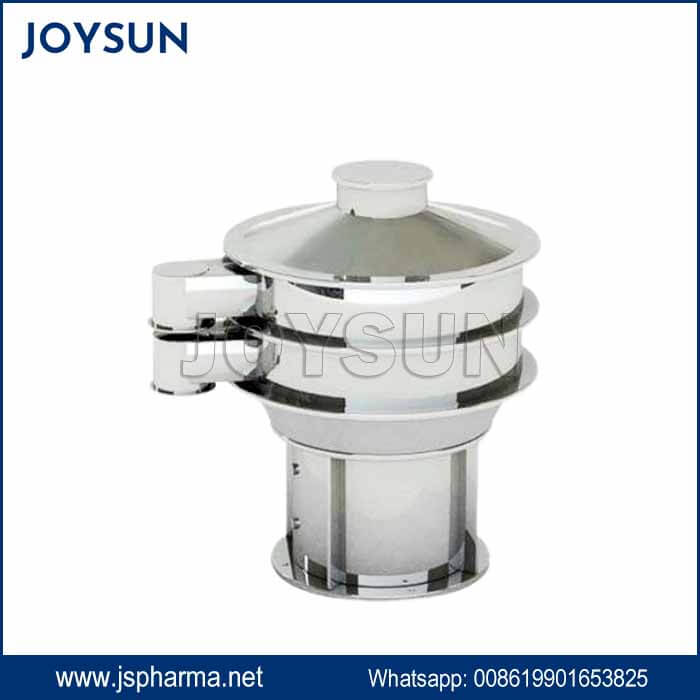
- Size Reduction System: Mills the compacted material into granules of desired sizes.
How does the dry granulation roller compactor work?
The working principle of a roller compactor for dry granulation can be broken down into three main stages:
- Feeding:
The dry powder blend is fed into the roller compactor using a screw feeding system. It consists of screw feeder, hopper, or other device that ensures a consistent and controlled flow of powder into the compaction chamber.
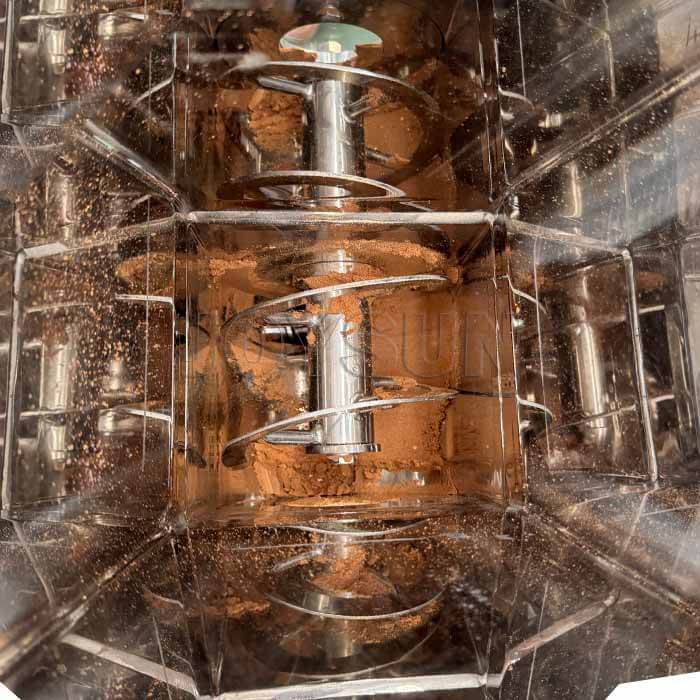
- Compaction:
The powder then enters the compaction chamber, which is the core part of the machine. It has two counter-rotating rollers. These rollers are either smooth or textured depending on the feeding material properties.
As the powder passes between the rollers, the rollers apply a significant amount of pressure. This pressure forces the individual powder particles together, densifying them and forming a compact sheet or flake of material. The thickness of the sheet is determined by the gap between the rollers, which is adjustable.
- Size Reduction:
The compacted sheet exiting the rollers is then fed into a size reduction unit/milling. It is a mill, grinder, or other equipment designed to break the sheet into different sizes of granule.
The final granules size is crucial due to below factors:
Flowability and handling: Smaller granules tend to flow and handle better during further processing, such as tableting or encapsulation. However, it doesn’t mean the smaller the better, too smaller granule.
Dissolution rate: In the case of pharmaceuticals, the size of the granules can affect how quickly a drug dissolves in the body.
What factors influence the dry granulating process:
Roller surface: The surface of the rollers can be smooth or textured. Textured rollers can be used to create granules with specific shapes or properties.
Roller speed: The speed of the rollers also impacts the compaction process. Slower speeds may be used for delicate materials, while faster speeds can be used for more robust materials.
Material properties: The properties of the powder itself, such as its particle size, density, and flowability, will influence the compaction process and the final characteristics of the granules.
By controlling these various factors, roller compaction allows for the production of uniform and well-defined granules from dry powders, making it a valuable tool in various industries.
What Advantages does Dry Granulation Have?
Simple Comparison between Dry and Wet Granulation
Powder Roller compactors are a primary method applied in powder dry granulation. It excels at below aspects:
Dry Operation: Unlike wet granulation, which uses a liquid binder, roller compaction works entirely with dry powders. This is crucial for materials that are sensitive to moisture or heat, which can be damaged by traditional wet methods.
Compaction and Densification: Roller compactors effectively press loose powders into denser sheets, flakes or biscuits. This improves the flowability and handling characteristics of the material, making it easier to process further into tablets or capsules.
Controlled Granule Size: After compaction, the flakes or sheets are milled into granules via screens. This allows for better control over the final product’s properties.
Simpler and faster process than wet granulation.
More energy-efficient due to the absence of drying steps.
Suitable for moisture- and heat-sensitive materials.
Offers good control over granule properties.
What industires is Dry Roller Compaction used?
Pharmaceutical: Creating tablets and capsules with consistent drug delivery.
Food: Processing ingredients for better handling and flowability.
Chemical: Producing granules for various chemical applications.